Planning flexibility
Following the demographics change previewed to the next 30 years, existing and new facilities shall consider its mutability to adjust to population needs gradually. Also, the climate change offers the opportunity to plan new facilities flexibility to accommodate the so far predictable climate changes, bearing in mind a level of adjustability to the climate change unforeseen events. Flexibility is one of the key answers for the health provision ageing and climate preparedness. Our planning method tables the levels of flexibility in health facilities in sectors: strategic, functional, constructive and operational flexibility:
Strategic Flexibility – this being the facilities possibility to expand existing departments or building new ones, vertically or horizontally. Or otherwise consider a phased facility development. Strategic flexibility shall be taken in account in planning, also considering the open degrees in the facility to extend temporary facilities, meant to be the answer at the disaster and climate change preparedness level. The location of vertical transportation means (lifts, staircases and ramps) inside the hospital building, play a vital role in deciding the degree of flexibility to expand. A provision of “soft spaces” adjacent to departments meant firstly as non-medical and convertible to expansion permanent or temporary.
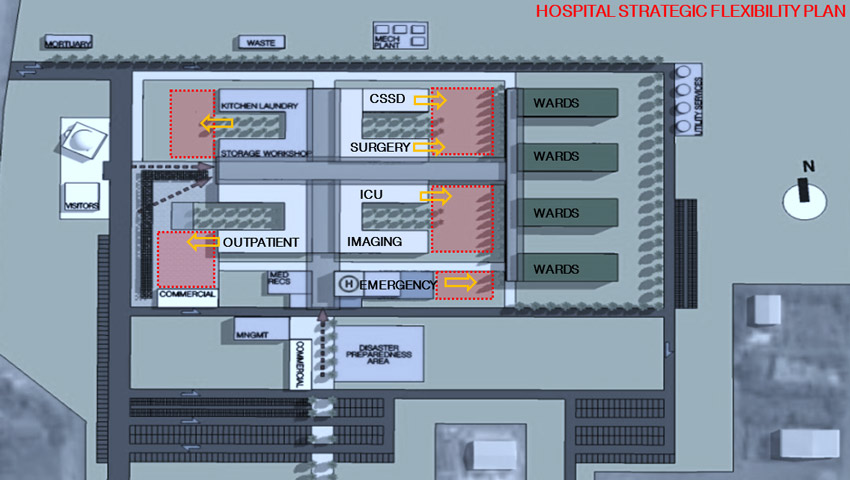
Above, the Aceh Hospital-type masterplan, designed in 2014. The different departments were intentionally planned with large gaps in between, to allow future expansions. To be noticed the large area close to the emergency department, planned as disaster preparedness area that would allow the emergency department to extend to there. This area was planned having in mind the patient treatment of a similar disaster to the 2004 south pacific tsunami.
Functional Flexibility – the multifunctional facility, aimed to be converted when needed, on different scales: wing, floor, department, room. At this level resides the importance of a structural grid wide openness, this being wide enough to allow all medical departments’ different equipment’s. This concept his referred in the reviewed literature as modularity. Aiming the higher-level in functional flexibility facility in Healthcare provision, the moveable and demountable the partition walls, the better; allowing a rapid swift in the facility to accommodate any unforeseen or as part of the modification preparedness.
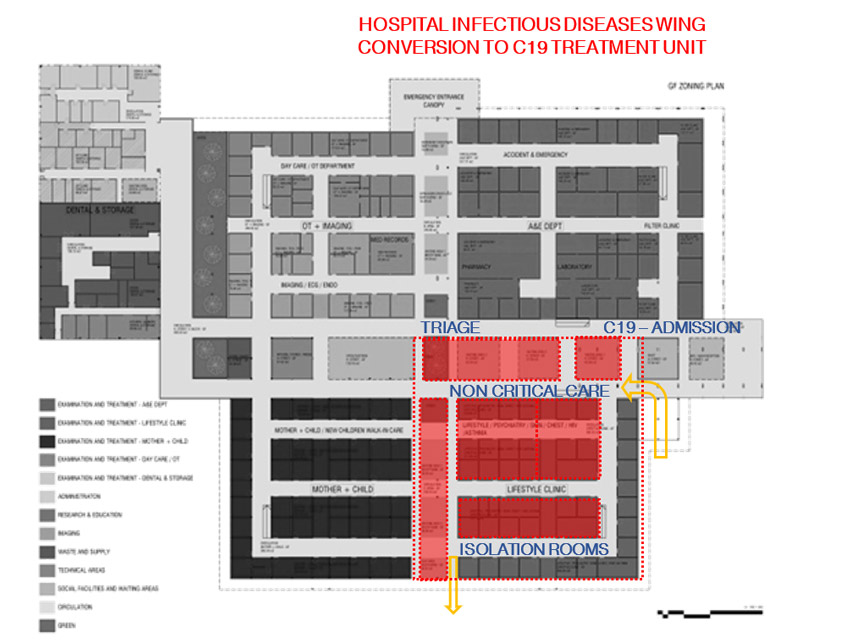
Above, the Arima Health Centre wing conversion to C19 treatment. The hospital planning mobility allows to dismantle internal walls to convert to isolation rooms. Part of the out-patient hospital can be converted to an infection pandemic treatment, while the emergency and surgery departments can keep working normally.
Constructive Flexibility – the non-medical infrastructures adaptability, convertibility and expandability, the facility preparation to change. The use of interstitial room aside functional spaces to be used in new infrastructures. Interstitial floors, ceiling height above floor to ceiling meant to accommodate a function conversion. Location of the electrical, mechanical and hvac back-bones, free space to convert.
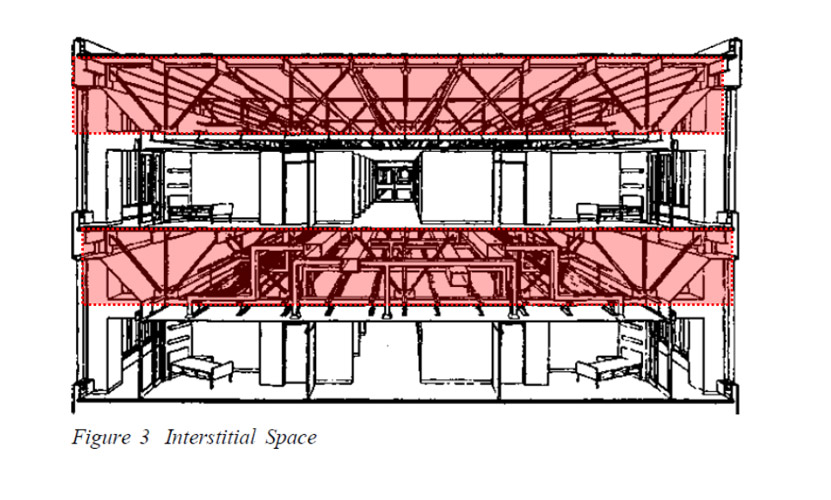
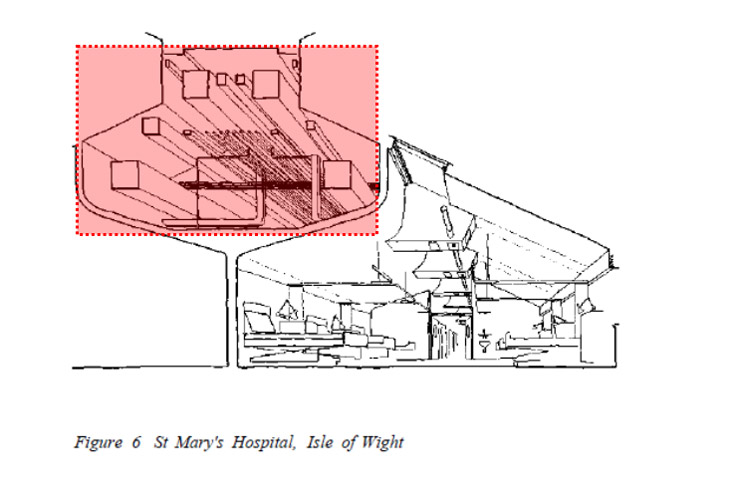
Operational Flexibility – the daily operations alteration possibilities. Modular furniture that can be configured in various ways is an example of operational flexibility. Consultation rooms often used for shorter duration in a day may be quickly configured for the rest of the day into another space, temporary office space, meeting rooms.